Intracranial Pressure Neuromonitoring: A Comprehensive Overview

Intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring is a critical tool in the management of neurocritical patients. By measuring the pressure within the skull, clinicians can assess the adequacy of cerebral perfusion and identify potential complications such as intracranial hypertension or herniation. ICP monitoring is typically performed using a variety of methods, including invasive and non-invasive techniques.
Intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring is the measurement of the pressure within the skull. It is used to assess the adequacy of cerebral perfusion and to identify potential complications such as intracranial hypertension or herniation. ICP monitoring is typically performed using a variety of methods, including invasive and non-invasive techniques.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 17465 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 342 pages |
Invasive ICP Monitoring
Invasive ICP monitoring involves the insertion of a probe into the brain parenchyma. This is typically done through a burr hole in the skull. The probe is connected to a pressure transducer, which measures the ICP and displays it on a monitor. Invasive ICP monitoring is the most accurate method of ICP measurement, but it is also the most invasive and carries a risk of complications such as infection, hemorrhage, and seizures.
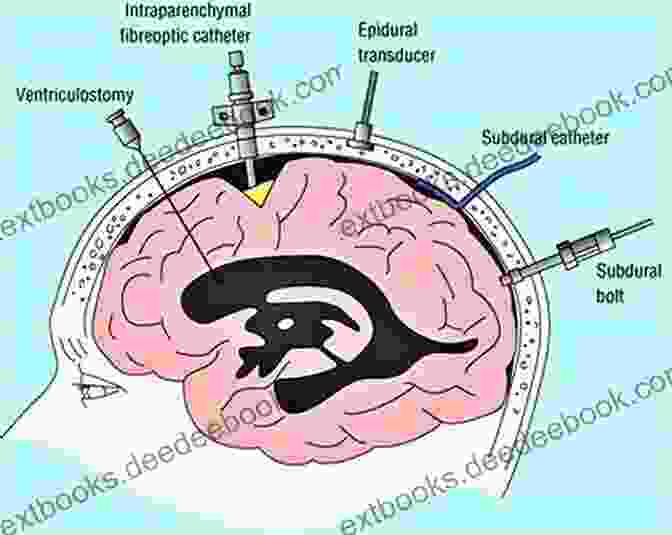
Non-invasive ICP Monitoring
Non-invasive ICP monitoring involves the use of a variety of techniques to estimate the ICP without inserting a probe into the brain. These techniques include:
* Transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCD): TCD uses ultrasound to measure the velocity of blood flow in the middle cerebral artery. Increased ICP can cause a decrease in blood flow velocity, which can be detected by TCD. * Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS): NIRS uses near-infrared light to measure the oxygen saturation of brain tissue. Increased ICP can cause a decrease in oxygen saturation, which can be detected by NIRS. * Optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD): ONSD is the diameter of the optic nerve sheath, which is a fluid-filled space that surrounds the optic nerve. Increased ICP can cause an increase in ONSD, which can be measured by ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Non-invasive ICP monitoring is less accurate than invasive ICP monitoring, but it is also less invasive and carries a lower risk of complications.
Indications for ICP Monitoring
ICP monitoring is indicated in patients who are at risk for developing intracranial hypertension or herniation. These patients include those with:
* Severe head injury * Subarachnoid hemorrhage * Intracerebral hemorrhage * Ischemic stroke * Brain tumors * Meningitis * Encephalitis
Management of ICP
The goal of ICP management is to maintain the ICP within a normal range (5-15 mmHg). This can be achieved through a variety of measures, including:
* Medical therapy: Medical therapy for ICP management includes the use of diuretics, osmotherapy, and hyperventilation. Diuretics can help to reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF),which can lower ICP. Osmotherapy involves the administration of hypertonic solutions, which can draw water out of the brain and lower ICP. Hyperventilation can also lower ICP by reducing the production of CO2, which can cause vasodilation and increased cerebral blood flow. * Surgical therapy: Surgical therapy for ICP management includes the placement of a ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt or a decompressive craniectomy. A VP shunt is a tube that is placed in the ventricles of the brain and drains CSF into the peritoneal cavity. A decompressive craniectomy involves the removal of a portion of the skull to allow the brain to expand.
ICP monitoring is a critical tool in the management of neurocritical patients. By measuring the pressure within the skull, clinicians can assess the adequacy of cerebral perfusion and identify potential complications such as intracranial hypertension or herniation. ICP monitoring is typically performed using a variety of methods, including invasive and non-invasive techniques. The choice of ICP monitoring method depends on the patient's clinical condition and the availability of resources.
References
1. Intracranial Pressure Monitoring in Neurocritical Care: American Association of Neurological Surgeons Guideline. Journal of Neurosurgery, Volume 129, Issue 1, Pages 11-23, July 2018. 2. Non-invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring: A Review of Current Methods. Frontiers in Neurology, Volume 10, Article 909, 2019. 3. Management of Intracranial Hypertension: A Multidisciplinary Approach. Neurohospitalist, Volume 8, Issue 4, Pages 222-238, 2018.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 17465 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 342 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Library
Library E-book
E-book Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Footnote
Footnote Codex
Codex Bestseller
Bestseller Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Thesaurus
Thesaurus Narrator
Narrator Character
Character Resolution
Resolution Card Catalog
Card Catalog Periodicals
Periodicals Scholarly
Scholarly Academic
Academic Journals
Journals Interlibrary
Interlibrary Study Group
Study Group Thesis
Thesis Storytelling
Storytelling Reading List
Reading List Book Club
Book Club Textbooks
Textbooks Lucas Gottman
Lucas Gottman Catherine Hernandez
Catherine Hernandez Danielle Trussoni
Danielle Trussoni Ross James
Ross James Elizabeth Laban
Elizabeth Laban Herbert J Rubin
Herbert J Rubin Taisen Deshimaru
Taisen Deshimaru Manuel Rivas
Manuel Rivas Wayne Mitchell
Wayne Mitchell Paula Nadelstern
Paula Nadelstern Cari Meister
Cari Meister David Lehman
David Lehman Beverley Driver Eddy
Beverley Driver Eddy James Hoag
James Hoag Will Glendinning
Will Glendinning Joseph Gutiz
Joseph Gutiz Lionel Smith
Lionel Smith Tobin Nellhaus
Tobin Nellhaus 1st Ed 2017 Edition
1st Ed 2017 Edition Dianne Wolfer
Dianne Wolfer
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Darren NelsonThe Secrets to Making Successful Telemarketing Cold Calls: A Comprehensive...
Darren NelsonThe Secrets to Making Successful Telemarketing Cold Calls: A Comprehensive... Ken FollettFollow ·7.2k
Ken FollettFollow ·7.2k Walt WhitmanFollow ·14.6k
Walt WhitmanFollow ·14.6k Pablo NerudaFollow ·2.2k
Pablo NerudaFollow ·2.2k Randy HayesFollow ·11.2k
Randy HayesFollow ·11.2k Drew BellFollow ·16.5k
Drew BellFollow ·16.5k Damon HayesFollow ·10.2k
Damon HayesFollow ·10.2k Chuck MitchellFollow ·17k
Chuck MitchellFollow ·17k Caleb LongFollow ·11.3k
Caleb LongFollow ·11.3k

 Elton Hayes
Elton HayesUnveiling the Enchanting Legends of Emelina Grace and...
Emelina Grace: The...

 Evan Simmons
Evan SimmonsWhat If Vietnam Never Happened: Foresight and Hindsight...
Published in 1955, Graham Greene's The Quiet...

 Camden Mitchell
Camden MitchellThe Rise of Specialty Coffee, Craft Beer, Vegan Food,...
In recent years,...

 Corey Hayes
Corey HayesModern Project Creative Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide...
In today's competitive business landscape,...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 17465 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 342 pages |